🤣Vulnerability #4: Lack of SSL Certificate Validation
An often overlooked part when testing mobile apps is checking whether the app properly verifies the validity of a given SSL certificate.

When a certificate is invalid or malicious, it might allow an attacker to spoof a trusted entity by interfering in the communication path between the host and client. The software might connect to a malicious host while believing it is a trusted host, or the software might be deceived into accepting spoofed data that appears to originate from a trusted host. Such is the case of com.insecureshop.WebViewActivity
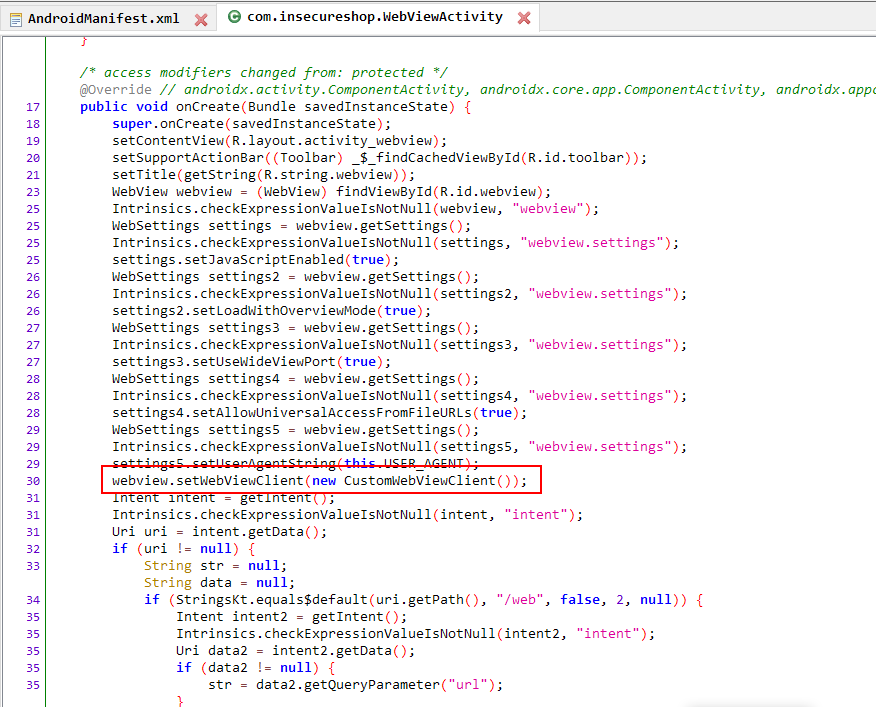
Checking the code above, we can see that WebViewActivity uses a CustomWebViewClient() object. Examining this class reveals the following block of code:

CustomWebViewClient overrides the onReceivedSslError method of its WebViewClient parent, but does not properly handle instances where the client actually receives invalid ssl certificates instead it ignores the error and continues to do handler.proceed().
For the proof-of-concept, we can simply try to intercept HTTPS requests even without having a valid SSL/proxy certificate installed on the device. If confirmed, then the app does not properly validate SSL certs.
One thing that might concern readers is that com.insecureshop.WebViewActivity isn’t really explicitly used anywhere in the application, even after reading every line of the source code. True, but when we check the manifest entry for the application we see that it defines a deeplink:
As an attacker, we can try to phish credentials from a target victim by using a malicious app to open up a deeplink with the following URI: insecureshop://com.insecureshop/web?url=facebook.com which then opens up facebook.com on the vulnerable webview.
POC Steps:
Make sure that you don’t have a valid, working certificate installed on your device.
Use the following guide to configure burp + your device’s wifi proxy settings BUT DO NOT INSTALL THE BURP CERTIFICATE: https://portswigger.net/support/configuring-an-android-device-to-work-with-burp
Fire up the following adb command which should open
google.comon the vulnerable webview:
Try to search some stuff up and intercept the request. If you are able to intercept the https request for your search query, then you have verified that the app does not properly validate SSL certs.

Last updated